Contents
The zero-trust model is based on assuming everything is hostile. Its core premise is the micro-segmentation of network resources and the isolation of individual workloads. The goal is to limit the attack surface by establishing granular security policies and monitoring. Furthermore, a zero-trust model protects against attacks by limiting the number of users accessing the network.
User Verification Mechanisms
While implementing Zero Trust is a complex process, organizations can apply it in small steps. For example, the first step is defining all resources and implementing proper user verification mechanisms. Next, only grant users the privileges they need and not the privileges they have. The Ekran System has the essential capabilities for access control and insider threat prevention to implement zero-trust security. In addition, it can help your organization implement zero-trust security by limiting the number of user accounts accessing critical information and services.
Excessive Privileges & Over Permissions
Zero-trust security requires that everything is monitored, and the network must be continuously monitored. Moreover, the infrastructure must be secure and protected against all possible threats. This approach is based on the principle of least privilege access. The least privilege access means users should have only the privileges needed to perform their jobs. This reduces the exposure of sensitive areas on the network. Unfortunately, it is common for users to be granted excessive privileges and over permissions. Once their credentials have been compromised, these user accounts become a huge risk.
Two-Part System
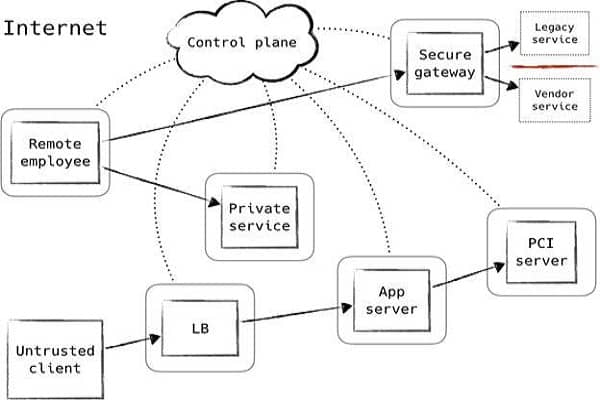
The Zero Trust security model uses a separate control plane. The data plane communicates application data. It is a two-part system. The first component is the lightweight agent sensor, which intercepts and enforces adaptive access control capability. The second component is the Policy Enforcement Point, which enforces the policy that limits access requests. The third component is the Policy Administrator, which authenticates the requestor and determines their authority dynamically. Only authenticated requests are granted access to corporate resources.
Also read: How IT Staffing Model Can Save A Fortune For Your Business
Traditional Network Security Model
The Zero Trust network consists of three components: a.zerotrust.net, software-defined perimeter, and VPN. A VPN is a network security solution, while the other two are the traditional computing environment. A traditional network security model relies on username, password, and ID tokens. With a zero-trust model, every device and network must be validated based on the user’s identity.
Zero Trust Network
The Zero Trust model limits the number of users a given user can access. Consequently, it also restricts access to only the authenticated users and has access to a particular service. The attackers can access sensitive information and exploit the system with a VPN. So, it’s essential to secure the data that is on the network. In a Zero Trust network, all users can access the same information.
A Zero Trust environment eliminates trusted users. It requires every user to authenticate. While single sign-on is useful, it often creates a security hole. Zero-Trust ensures that everyone is authenticated by limiting the number of users who can access the system. With a centralized identity, a trustless system limits access a user can have. Further, a zero-trust environment reduces the number of untrusted users.
Network Hosts & Users
A Zero Trust environment also limits the number of network hosts and users. By definition, a zero-trust enterprise requires at least two. A firewall, VPN, and proxy server are the most common forms of network security. Each of these systems should be able to provide these. In addition to firewalls, the security model must also include software. This architecture should be flexible and be scalable. Its benefits are clear.
Conclusion:
Zero Trust networks are highly adaptable and flexible. The Zero Trust model has three main components: virtual private networks and cloud infrastructure read more. The virtual network is a “network.” A network can have many different identities. The zero-Trust network is not a one-dimensional world. It can have a highly-integrated security model. Its most important component is the firewall.